
How to Create Interactive Dashboards in Excel: Easy Guide
Share
Understanding What Makes Excel Dashboards Truly Interactive

What distinguishes a truly interactive Excel dashboard from a static collection of charts? It's the power of dynamic data exploration. A basic chart offers a single snapshot, but an interactive dashboard is a richer experience. Think of it as a movie: users can rewind, fast-forward, and zero in on specific scenes. This dynamic exploration is key to uncovering hidden insights and driving data-informed decisions.
Key Elements of Interactivity
Several key features in Excel allow you to build this interactivity.
-
PivotTables: These tools summarize and categorize large datasets, enabling quick analysis. A PivotTable can summarize sales data by region, product, or any relevant time period.
-
PivotCharts: These visualize the data within a PivotTable, offering dynamic charting that updates as the underlying PivotTable changes.
-
Slicers: These user-friendly controls act as filters for your dashboard. Users can filter data by criteria like product category or date range with a single click.
-
Dynamic Charts: These charts automatically update based on user selections made with slicers or other interactive elements.
Creating interactive dashboards in Excel transforms raw data into a dynamic, explorable format, providing insights at a glance. By using PivotTables, PivotCharts, and Slicers, you can summarize data and give viewers the power to interact with it. This unlocks a deeper understanding of the data's story, as users filter, sort, and display information according to their needs. Learn more here: Creating Interactive Dashboards in Excel.
The Power of User Control
These elements give users control over the data they see.
- They choose which metrics to focus on.
- They decide how to filter the data.
- They control the level of detail.
This transforms passive viewing into active exploration, leading to better understanding and smarter decisions. For more tips and techniques, check out this resource: How to master data scrubbing techniques.
Consider a sales dashboard. Interactive elements let a sales manager quickly filter data to see performance by region, product, or even individual salesperson. They can identify trends, spot outliers, and make informed decisions about resource allocation. This level of interactivity simply isn’t possible with static charts.
Preparing Your Data Foundation For Dashboard Success
Creating interactive dashboards in Excel relies heavily on a well-structured data foundation. This crucial preparation is what separates insightful, successful dashboards from confusing, error-prone spreadsheets. Think of your data like the ingredients for a recipe: even the most skilled chef can't create a culinary masterpiece from spoiled or disorganized components.
Structuring Your Data
First, organize your data into a proper Excel Table. This isn't just about aesthetics; it unlocks helpful features like automatic formula propagation and dynamic range naming. A structured table makes data analysis much more efficient, just like a well-organized pantry simplifies cooking. You might be interested in: How to master data transformation with Power Query.
-
Clear Column Headers: Use descriptive headers to clearly identify each data point. Avoid jargon or abbreviations that might confuse others.
-
Consistent Formatting: Maintain consistent formatting within each column. This ensures data integrity and allows for accurate calculations and filtering.
-
Data Validation: Implement data validation rules to prevent incorrect entries. This acts as a quality control check, ensuring the accuracy of your dashboard's source data by catching errors before they impact your dashboard.
Cleaning and Transforming
Next, address data quality issues. This data cleaning process involves handling missing values and correcting any errors. Much like a chef removes impurities before cooking, you need to remove or correct imperfections within your data.
-
Missing Values: Decide how to handle missing data. Options include removing rows with missing values, replacing them with a placeholder or an average, or leaving them blank if appropriate. Select the approach that best suits your analysis goals.
-
Error Correction: Identify and correct any data entry errors or inconsistencies. This might involve validating formulas, checking for typos, or ensuring consistent formatting.
Establishing Relationships
Finally, if your dashboard pulls data from multiple sources, clearly define the relationships between them. This is essential for creating accurate calculations and dynamic filtering. Think of it like building a house: without understanding the connections between the foundation, walls, and roof, the structure would be unstable. Similarly, your dashboard requires clear data relationships to function effectively.
-
Lookup Tables: Use lookup tables to connect related information from different sources. This allows for dynamic filtering and aggregation based on related data points.
-
Data Model: For complex relationships, consider creating a data model using Power Pivot. This provides a robust framework for managing and analyzing large datasets from multiple sources, especially beneficial when dealing with complex relationships and large amounts of data.
Building Your First Interactive Components That Actually Work
Creating interactive dashboards in Excel empowers users to explore data and uncover hidden insights. This goes beyond simply adding visual flair; it's about enhancing understanding through practical interactivity.
Mastering PivotTables and PivotCharts
The foundation of interactive dashboards often lies in PivotTables. These tools summarize large datasets, allowing for dynamic grouping and analysis by different categories. Think of them as customizable report generators built into Excel.
-
Start with a Solid Data Source: Clean, organized, and correctly formatted data ensures your PivotTable operates smoothly and yields accurate results.
-
Strategic Field Placement: The power of PivotTables is in dragging and dropping fields into Rows, Columns, Values, and Filters. Experiment to uncover different data perspectives.
-
Calculated Fields: Add another layer of analysis with calculated fields, performing custom calculations within the PivotTable itself.
Once your PivotTable is set, creating a PivotChart is easy. Directly linked to the PivotTable, these charts update dynamically as you adjust the PivotTable's layout or filters. This visual representation adds clarity and impact. Read more about creating interactive reports here: How to master building stunning interactive reports in Excel
Empowering Users with Slicers
Slicers are the user-friendly controls of interactive dashboards, acting like filters for specific data point analysis. They provide a simple way to filter data by various criteria, such as region, product, or time period.
-
Connect to Multiple PivotTables: A single slicer can control multiple PivotTables and PivotCharts, creating a cohesive analytical experience. Changes made using one slicer update all connected elements.
-
Visual Appeal and Clarity: Slicers are visually appealing and can be customized to match your dashboard's design. Maintain clear labels and an intuitive organization.
-
Strategic Placement and Grouping: Arrange slicers thoughtfully to guide users through the data. Group related slicers to improve usability and avoid clutter.
Connecting Interactive Elements
The real power comes from connecting multiple components. Selecting a specific product category using a slicer can update the PivotTable to show relevant sales data and simultaneously update the PivotChart to visualize the results. This creates a dynamic and engaging data exploration experience.
The following infographic shows key data on average dashboard build time (hrs), average data refresh time (secs), and interactive user engagement rate (%).
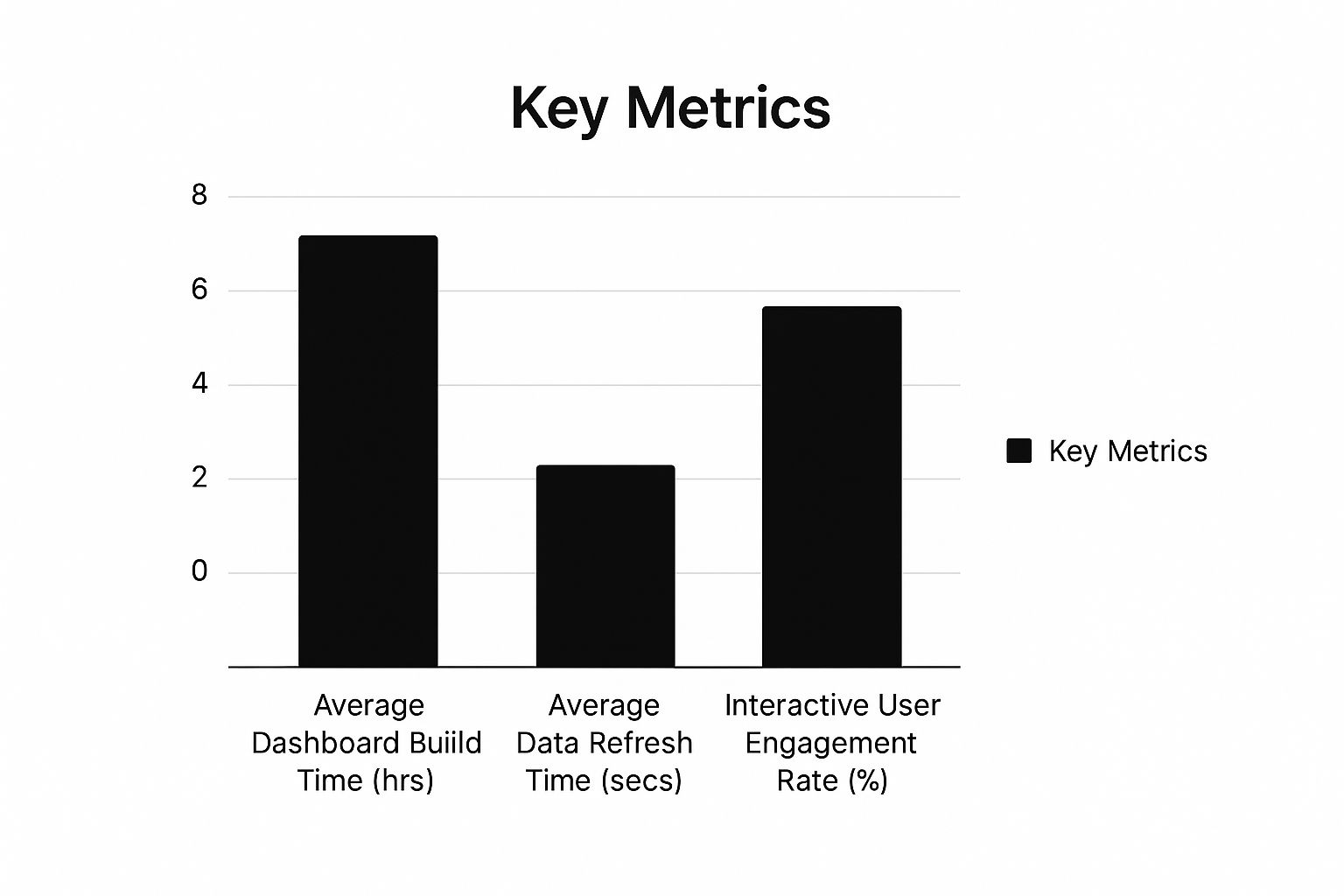
While interactive dashboards might require a slightly longer build time, the increased user engagement and fast refresh times demonstrate the value of interactivity. This transforms passive viewers into active explorers, leading to better insights and decision-making.
To understand different interactive elements better, let's look at a comparison table:
The following table compares various interactive elements in Excel dashboards. It highlights their primary functions, best use cases, and complexity levels.
Interactive Elements Comparison
| Element Type | Primary Function | Best Use Case | Complexity Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| PivotTable | Summarizing and analyzing large datasets | Exploring sales data by region and product | Medium |
| PivotChart | Visualizing data from a PivotTable | Displaying trends and patterns in sales data | Medium |
| Slicers | Filtering data in PivotTables and PivotCharts | Allowing users to select specific product categories | Easy |
| Form Controls (Buttons, Checkboxes) | Triggering macros and actions | Running specific reports or calculations | Advanced |
Combining PivotTables, PivotCharts, and slicers creates a cohesive and user-friendly analytical environment within Excel.
Advanced Visualization Techniques That Tell Compelling Stories

Building interactive dashboards in Excel involves more than simply placing charts on a spreadsheet. It's about creating a visual narrative that effectively communicates the story within your data. This means going beyond the basics and exploring advanced visualization techniques to enhance understanding and engagement.
Dynamic Charts: Responding to User Input
Creating dynamic charts is key for interactivity. These charts change automatically based on user selections, enabling a deeper exploration of the data.
For example, connecting a chart to a slicer lets users filter data by specific criteria. The chart instantly updates to reflect the selected information. This real-time responsiveness changes how users interact with the data, helping them uncover insights relevant to their specific needs.
Combination Visualizations: Revealing Complex Relationships
Sometimes, one chart isn't enough. Combination visualizations, blending multiple chart types, can reveal complex relationships within your data.
Imagine combining a line chart showing overall trends with a bar chart highlighting individual data points. This allows viewers to see both the overall picture and the specific details simultaneously. This layered approach enhances the understanding of complex datasets.
Conditional Formatting: Highlighting Key Insights
Conditional formatting is more than just aesthetics. Used strategically, it highlights critical insights without overwhelming the viewer.
Color-coding cells based on value ranges draws attention to outliers or important trends. This makes it easier to spot key data points at a glance, adding an analytical layer to your dashboard and guiding users toward the most relevant information.
Choosing the Right Visualization
Selecting the right visualization is crucial. A pie chart might be suitable for displaying proportions, while a scatter plot is better for showing correlations. You might be interested in: How to master data visualization best practices. Carefully consider your data and your audience to choose the most effective chart type.
Advanced Formatting: Professional Polish
A well-formatted dashboard is more credible and engaging. Consistent use of fonts, colors, and layout creates a professional, polished appearance. However, prioritize clarity and usability over excessive design elements. A clean, well-organized dashboard is more effective than a visually cluttered one.
Handling Visualization Challenges
Dashboards often encounter challenges such as large datasets or multiple metrics. Consider using techniques like data aggregation to summarize large datasets before visualizing them.
For multiple metrics, use small multiples. These are miniature versions of the same chart, each displaying a different metric. This allows for comparison across metrics while keeping the dashboard concise.
Breaking the Rules: Custom Visualizations
Sometimes, standard chart types just aren't enough. Don't be afraid to break conventional charting rules and create custom visualizations that better suit your specific needs. This might involve combining elements of different chart types or creating entirely new ways to visually represent your data. The goal is to tell your data's story in the most impactful way possible.
Optimizing Performance And Creating Exceptional User Experiences
A visually appealing dashboard loses its effectiveness if it's slow, confusing, or prone to crashing when handling data. Think of it like a sports car with a roaring engine but unreliable brakes – impressive on the surface, but ultimately lacking control. This section explores techniques to optimize performance and ensure your Excel dashboards remain responsive, even with large datasets. We'll also cover user interface design principles specifically for Excel, creating dashboards that are both powerful and user-friendly.
Performance Optimization Strategies
Performance issues in Excel dashboards often arise from inefficient formulas, excessive formatting, or poorly structured data. These problems can lead to frustrating delays and impact the user experience. Optimizing these elements is essential for a smooth and efficient dashboard.
-
Efficient Formulas: Avoid volatile functions like
NOW()andTODAY()within cells that don't require dynamic updates. Place these in a dedicated cell and reference them elsewhere. This simple change prevents unnecessary recalculations, keeping your dashboard responsive. -
Streamlined Formatting: Conditional formatting, while visually helpful, can consume significant resources. Use it strategically, highlighting key insights rather than applying it across entire worksheets. This targeted approach helps maintain performance.
-
Data Tables: Organize your data into proper Excel Tables. This not only improves performance but also allows for dynamic range naming, simplifying formulas and maintenance.
User Interface Design For Excel Dashboards
User interface (UI) and user experience (UX) design principles are crucial for dashboard effectiveness. A well-designed dashboard should guide users seamlessly through the data story, providing clear insights without overwhelming them. Read also: How to master Excel report automation.
-
Clear Layout: Organize dashboard elements logically, placing the most important information prominently. Use clear headings and labels to guide users through the data.
-
Intuitive Navigation: Incorporate interactive elements like slicers and dropdowns to empower users to filter and explore the data effortlessly. Ensure these controls are clearly labeled and positioned intuitively.
-
Visual Hierarchy: Use visual cues like font size, color, and spacing to establish a clear hierarchy of information. This draws attention to key insights and enhances readability.
Interactive dashboards in Excel are increasingly important for organizations seeking to optimize operations and make data-driven decisions. Creating dashboards that are both functional and adaptable to different stakeholders' needs ensures data analysis is effective and accessible. For example, a company might create a dashboard to track employee productivity across various departments. Using Excel's advanced features, the dashboard can offer real-time performance insights, enabling managers to identify areas needing training or better resource allocation. Learn more about interactive dashboards here: FasterCapital on Excel Dashboards.
Testing and User Feedback
Testing your dashboard with actual users is essential. This helps identify areas for improvement and ensures the dashboard truly meets user needs.
-
Usability Testing: Observe how users interact with the dashboard. Do they easily find the information they need? Are the interactive elements intuitive?
-
Feedback Collection: Gather feedback through surveys or interviews. Ask users what they like and dislike about the dashboard, and what could be improved.
-
Iterative Design: Use the feedback gathered to refine your dashboard. This iterative process ensures a user-centered approach and increases adoption rates. Think of it like polishing a gem – each iteration brings it closer to perfection.
By prioritizing both performance and user experience, you can create Excel dashboards that are not just visually appealing but also powerful tools for data analysis and decision-making. This combination of form and function is essential for maximizing the impact of your data insights.
Real-World Success Stories and Business Impact

Interactive dashboards in Excel are more than just pretty reports. They deliver real business results across diverse industries. By giving users the power to explore data dynamically, these dashboards lead to smarter decisions, better resource allocation, and improved overall operational efficiency.
Measurable Improvements With Interactive Dashboards
Let's look at some specific examples of how interactive Excel dashboards have made a tangible impact:
-
Sales Performance Tracking: A sales team used an interactive dashboard to monitor their quarterly performance. With slicers in Microsoft Excel, they could quickly analyze sales by region, product, and individual salesperson. This targeted approach resulted in a 15% sales increase.
-
HR Recruitment Metrics: An HR department used a dashboard to keep an eye on key recruitment metrics. Visualizing time-to-hire and cost-per-hire allowed them to pinpoint bottlenecks and reduce hiring time by 20%.
-
Inventory Management: A retail company implemented a dashboard to better manage inventory levels. By dynamically monitoring stock and sales trends, they reduced inventory holding costs by 10% and minimized stockouts.
These examples show how versatile and effective interactive Excel dashboards can be in driving measurable improvements across different business functions.
Calculating Return on Investment (ROI)
Showing the ROI of dashboard initiatives is key for getting buy-in and justifying ongoing investment. This means quantifying the benefits gained. For example, a decrease in report generation time can be translated directly into cost savings.
-
Time Saved: Determine how much time is saved by automating reporting processes and data analysis with the dashboard.
-
Improved Decision-Making: Estimate the financial impact of the sounder decisions made thanks to dashboard insights.
-
Increased Efficiency: Measure the efficiency gains achieved by streamlined workflows and optimized resource allocation.
By tying these benefits to financial outcomes, you can build a strong business case for dashboards and show their value to stakeholders. Beyond enhanced data analysis, interactive Excel dashboards also play a crucial role in optimizing resource use. Learn more about Microsoft 365 usage and adoption here: AdminDroid.
Scaling Dashboard Programs Across Organizations
Successfully scaling dashboard initiatives across larger organizations takes careful planning and execution. This includes addressing key challenges:
-
Data Governance: Establish clear data governance policies to ensure data accuracy and consistency across all dashboards.
-
Training and Support: Give users sufficient training and support to use and interpret the dashboards effectively.
-
Standardization: Implement standardization guidelines for dashboard design and development for consistency and easier maintenance.
By tackling these challenges, organizations can maximize the impact of their dashboard programs and build a truly data-driven culture.
Scaling Your Dashboard Success For Long-Term Impact
Building an interactive dashboard in Excel is just the first step. Maintaining its accuracy, sharing it effectively, and adapting it to evolving needs are crucial for long-term success. This requires a proactive approach and strategic planning.
Maintaining Accuracy and Currency
A dashboard's value diminishes if its data is outdated. Implementing automated data refresh strategies is essential.
-
Data Connections: Connect your dashboard directly to data sources, such as other Excel files, databases, or online platforms. Excel can automatically refresh these connections on a schedule. This keeps your dashboard data current without any manual intervention.
-
Power Query: For more complex data transformations and integrations, consider using Power Query. This powerful tool allows you to pull data from multiple sources, clean and transform it, and then load it into your dashboard. Power Query also offers automated refresh capabilities.
Version Control and Collaboration
As your team grows and multiple users interact with the dashboard, version control becomes essential. This prevents conflicting edits and ensures everyone works with the most up-to-date version.
-
Shared Workbooks: Excel's built-in shared workbook feature allows multiple users to work on the same file simultaneously. However, be aware that this can sometimes lead to conflicts.
-
Cloud Storage: Consider storing your dashboard in cloud services like OneDrive or SharePoint. These platforms enable version history, allowing you to revert to previous versions if needed. They also offer valuable collaboration features, making it easier for teams to work together.
Sharing Your Dashboard Effectively
Sharing your insights is the ultimate goal. Choosing the right sharing method depends on your audience and security needs.
To help you choose, here's a comparison of different sharing methods:
Dashboard Sharing Methods
| Sharing Method | Security Level | Collaboration Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Emailing Excel File | Low | Limited | Individual sharing |
| Shared Workbook | Medium | Real-time co-authoring | Small team collaboration |
| OneDrive/SharePoint | High | Version history, co-authoring | Larger teams, controlled access |
| PDF Export | High | No collaboration | Static reports |
| Excel Online | Medium | Web-based viewing and editing | Broad access |
This table highlights the key differences in security and collaboration features, helping you select the most suitable method for your specific needs. For high security and robust collaboration, cloud storage solutions offer the best balance.
Building a Dashboard Culture
Integrating dashboards into your organization’s workflow maximizes their impact. This involves fostering a data-driven culture.
-
Training and Support: Equip users with the skills and knowledge to interact with and interpret dashboards effectively.
-
Regular Updates and Maintenance: Keep your dashboards up-to-date and responsive. This ensures they remain relevant and continue providing valuable insights.
-
Feedback and Iteration: Encourage user feedback and use it to improve the dashboard’s design and functionality. This iterative process ensures the dashboard remains user-centered and meets evolving needs.
Expanding Your Skills
Your dashboard journey doesn’t end here. Continuously expanding your skills will enhance your ability to create even more powerful and impactful dashboards.
-
Advanced Excel Features: Explore advanced Excel features like VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) to automate tasks and add custom functionality.
-
Data Visualization Best Practices: Keep learning about effective data visualization techniques to present data clearly and compellingly.
-
Other BI Tools: Consider exploring other business intelligence (BI) tools like Power BI for advanced data analysis and visualization capabilities.
By following these strategies, your dashboards will remain valuable assets, driving informed decision-making and contributing to long-term success. Ready to level up your Excel skills? Visit SumproductAddict for witty Excel-themed apparel and accessories!