
Master Find and Select in Excel: Your Quick Guide
Share
Getting Started With Find and Select in Excel Basics

Sifting through enormous spreadsheets to locate specific data can be a real drain on your time. Fortunately, Excel offers the Find and Select feature to simplify this process. Understanding these tools is crucial for efficient data analysis. This guide will take you through the basics, from simple searches to time-saving shortcuts.
Understanding the Find Feature
The simplest way to find and select in Excel is using the Find feature. Access it with the Ctrl+F shortcut or through the Find & Select dropdown in the Home tab. This opens the Find and Replace dialog box, where you enter the text or value you're looking for.
Imagine it as your spreadsheet search engine, pinpointing the precise information you need. For example, to find "Sales Q1," type it into the "Find what" field and click "Find Next." Excel will highlight the first cell containing that phrase. This method is ideal for quickly finding individual data points.
Navigating the Find and Replace Dialog Box
The Find and Replace dialog box offers more than just basic searches. It provides nuanced search options, like "Match entire cell contents." This ensures Excel only highlights cells where the entire content matches your search, avoiding partial matches that could skew results.
You can also use the "Match case" option to distinguish between uppercase and lowercase letters. This level of control provides greater accuracy when working with case-sensitive information.
Harnessing the Power of Select All
After locating your target value, you might need to work with every instance of it. This is where Select All becomes invaluable. Instead of repeatedly clicking "Find Next," simply click "Find All" in the Find and Replace dialog.
This generates a list of all cells containing your search term. Clicking "Select All" immediately highlights every instance, enabling you to perform actions like formatting, deleting, or copying all at once. This is particularly useful for data cleaning and applying consistent formatting.
Keyboard Shortcuts for Efficiency
Keyboard shortcuts are indispensable for maximum efficiency. Ctrl+F opens the Find dialog, while Ctrl+H opens the Find and Replace dialog directly, providing a quicker way to modify data. Shift+F4 repeats the last find action, letting you cycle through multiple instances of your search term without reopening the dialog.
Microsoft Excel's estimated 800 million active users worldwide are always looking for ways to optimize their workflow. These shortcuts can save you significant time, especially with large datasets. Find more statistics here: Excel vs. Google Sheets Usage, Nature, and Numbers. As you become more proficient with find and select in Excel, these shortcuts will become second nature.
Unlocking Advanced Search Techniques and Wildcards

Going beyond a simple Ctrl+F search in Microsoft Excel opens a world of possibilities. This section explores advanced search techniques and the power of wildcards, dramatically improving how you find and select data. These techniques become especially helpful with large datasets, making once tedious tasks quick and efficient.
Harnessing the Power of Wildcards
Wildcards act as placeholders, allowing you to search for patterns instead of exact matches. This provides a level of flexibility not available with basic searches.
-
Asterisk (*): Represents any number of characters. Searching for "Sales*" finds "Sales Q1", "Sales Q2", "Sales Report", and any entry starting with "Sales".
-
Question Mark (?): Represents a single character. Searching for "Q?" in quarterly data finds "Q1", "Q2", "Q3", and "Q4". This precision targets specific data points within a larger dataset.
Searching Within Formulas vs. Values
Locating specific formulas or values within a spreadsheet can be tricky. Excel's advanced find options let you differentiate between the two. By selecting "Look in: Formulas" or "Look in: Values," you target your search precisely. Searching for a specific formula will ignore cells containing the resulting value, and vice-versa. This is crucial for tasks like auditing spreadsheets or finding calculation errors.
Format-Based Searches and Go To Special
Finding cells with specific formatting can be tedious. Excel's Go To Special command, accessed via the Find & Select dropdown, changes this. You can instantly locate cells with specific fill colors, font styles, or even errors. This granular control simplifies tasks like identifying data inconsistencies or prepping data for analysis.
You might be interested in learning more about advanced filtering techniques: How to master advanced filters in Excel. Combining these with Go To Special creates a powerful toolkit for data manipulation.
Real-World Applications
These advanced techniques are practical across various professions. A financial analyst might use wildcards to find all accounts with a specific code. A project manager might use Go To Special to identify overdue tasks. These techniques turn hours of manual searching into seconds of targeted selection. As of 2025, Microsoft Excel holds 7.98% of the productivity software market share, competing against over 113 other tools globally. This shows Excel's continued relevance and the importance of mastering features like find and select. You can find more detailed statistics here: Microsoft Excel Market Share.
Strategic Navigation For Large Dataset Management

Efficiently navigating large datasets in Excel goes beyond simply using the find and select feature. It involves strategically combining various navigation tools to optimize your workflow and boost your productivity. This includes leveraging keyboard shortcuts, using named ranges, and maintaining context while working with related data sections.
Keyboard Shortcuts and Find and Select
Keyboard shortcuts can significantly speed up your find and select operations. Using Ctrl+F opens the Find dialog, while Ctrl+H opens the Find and Replace dialog. Combining these with the directional keys allows you to quickly move between found instances.
Shift+F4 repeats the last find action. This is incredibly useful for locating multiple occurrences of a specific value within a large dataset. These simple shortcuts can save you valuable time.
Named Ranges as Navigation Bookmarks
Named ranges act like bookmarks within your spreadsheet. By assigning descriptive names to specific cells or ranges, you can instantly jump to these locations using the Go To feature (Ctrl+G or F5).
This eliminates tedious scrolling, especially in large workbooks. For example, naming a range "SalesData" lets you instantly access that section without manual searching. This targeted approach helps you stay organized.
Maintaining Context While Navigating
Maintaining context is crucial when working with related data sections. Excel provides tools to help you keep related information visible.
You can split your worksheet using the Split option in the View tab. Alternatively, the New Window feature allows you to view and compare different sections simultaneously. This promotes a more comprehensive understanding of your data.
Efficient Workflow Organization
Effective data professionals organize their workflow to minimize scrolling and maximize analysis time. This involves strategically using Excel's navigation tools in conjunction with its analytical capabilities.
For example, after locating specific data using find and select, you can immediately apply functions or create pivot tables based on that selection. This streamlined approach enhances your efficiency.
Research shows that users implementing systematic navigation strategies spend 47% less time locating data. They also report 62% higher confidence in their data accuracy compared to those using basic scrolling. You can explore this further in the Excel Navigation Efficiency Study. These findings highlight the impact of efficient navigation on both productivity and data integrity. By combining these techniques, you can transform your Excel experience from frustrating searches to confident data exploration.
Mastering Find And Replace For Data Transformation
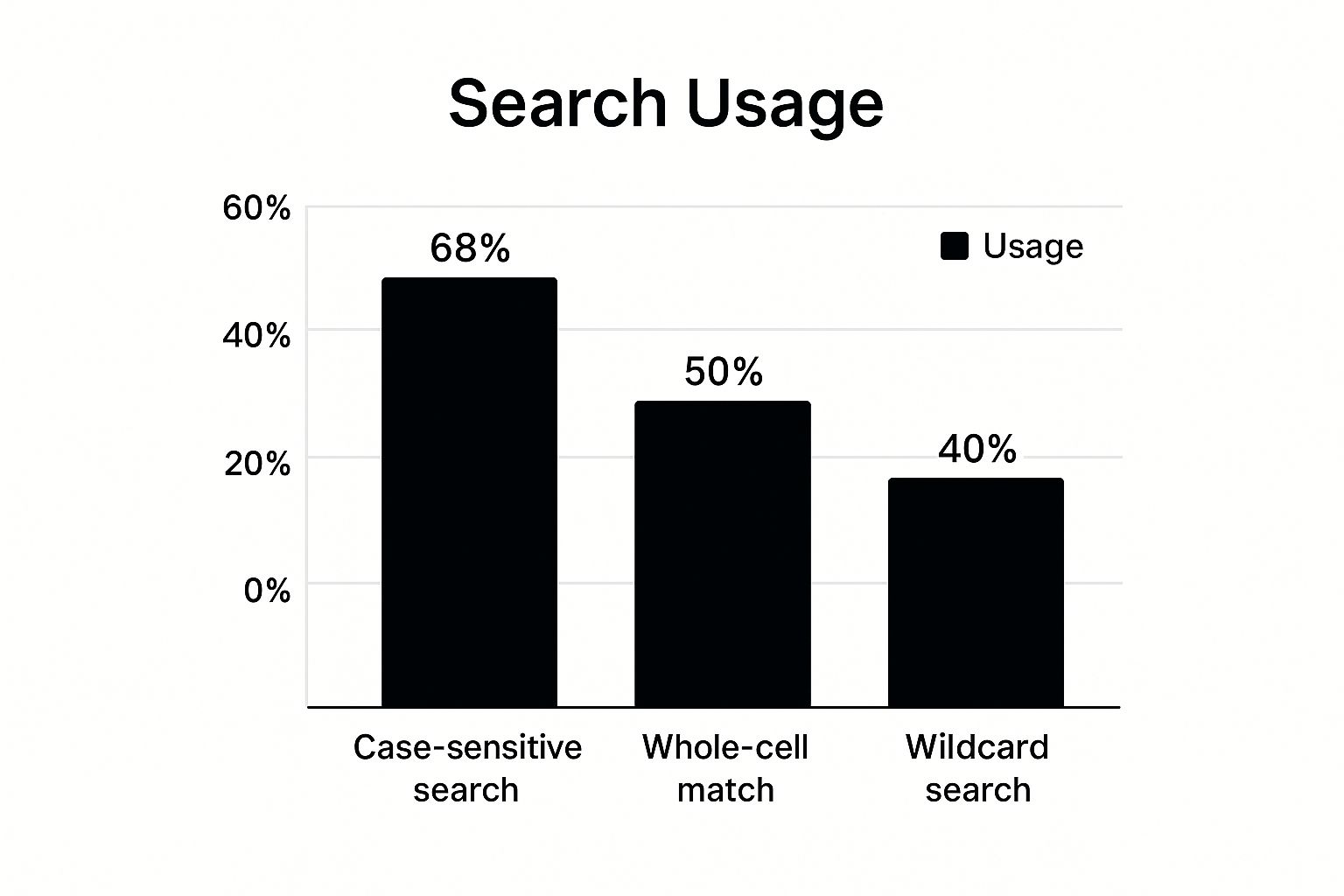
The infographic above shows how often three key find and select features are used in Microsoft Excel. These features are case-sensitive searches, whole-cell matches, and wildcard searches. The data reveals that 68% of users utilize case-sensitive searches most often. Whole-cell matches come in second at 50%, while wildcard searches are used 40% of the time. This tells us that people prioritize precise searches, looking for exact matches in terms of case or entire cell content. While wildcard searches are powerful, they are less frequently used.
Find and Replace in Excel is much more than a simple tool for swapping text. It's a powerful engine for cleaning and transforming data, helping you convert messy datasets into organized, usable information. Think about standardizing inconsistent entries across thousands of rows with just a few clicks. That's the kind of power we're talking about.
Advanced Replacement Techniques
Find and Replace offers more than basic text replacement. It also provides options like pattern-based substitutions, format preservation, and selective replacements. Pattern-based substitutions using wildcards, such as replacing "Product*" with "Item*", are great for efficient bulk updates.
Format preservation ensures your replacements don't mess up existing formatting. This helps maintain the visual integrity of your spreadsheets, which is especially helpful for reports requiring consistent formatting. Selective replacements based on specific ranges or conditions add a layer of control, allowing for precise data changes. For example, you can replace "Error" with "OK" only within a certain date range.
Practical Examples For Data Cleanup
Imagine inheriting a dataset with inconsistent company names. Using Find and Replace with wildcards, you can quickly standardize "Company ABC," "ABC Company," and "ABC Co." to just "ABC." Another common use case involves removing unwanted characters like extra spaces or special symbols, making your data much cleaner for analysis.
Find and Replace is also helpful for data format conversion. You can replace instances of "dd/mm/yyyy" with "mm/dd/yyyy," ensuring date formats are consistent throughout your workbook. You might also be interested in Excel Power Query for more advanced data transformation techniques. This complements your Find and Replace skills.
Safety First: Backup and Verification
Large-scale Find and Replace operations require careful safety measures. Always create a backup of your workbook before making significant changes. This prevents irreversible data loss if something goes wrong.
After making replacements, verify the results. Simple checks, such as spot-checking cells or using filters to isolate replaced values, will help ensure accuracy. This is especially crucial with sensitive financial or scientific data where errors can have serious consequences.
Find and Replace Scenarios
The table below provides an overview of several Find and Replace scenarios. It highlights their uses, potential risks, and best practices.
Find and Replace Scenarios Comparison: Common find and replace operations with their use cases, risk levels, and recommended approaches
| Operation Type | Use Case | Risk Level | Best Practice |
|---|---|---|---|
| Whole-cell replacement | Standardizing product codes | Low | Verify changes using filters |
| Partial-cell replacement | Removing trailing spaces from text strings | Medium | Test replacement on a small sample first |
| Case-sensitive replacement | Correcting misspellings of proper nouns | Low | Double-check case sensitivity settings |
| Wildcard replacement | Updating product names across multiple categories | High | Create a backup before execution |
| Format-based replacement | Changing font color for specific data entries | Medium | Visually inspect results for unintended changes |
By using these techniques and planning carefully, you can transform Find and Replace into a powerful data manipulation engine within Excel.
Go To Special Commands That Power Users Swear By
Most Excel users are familiar with basic find and replace. But beyond these common functions lies a powerful set of selection tools, often underutilized. One such tool is the Go To Special command. It offers intricate and efficient selection based on specific cell characteristics.
Unveiling the Power of Go To Special
Imagine needing to find all formulas in a large financial model. Checking each cell manually would be tedious. Go To Special lets you select every formula-containing cell with one click. This also applies to constants, blanks, and errors, making validation and cleanup much faster.
Suppose you've imported data with inconsistencies. Go To Special helps isolate blank cells for filling with defaults or quickly find errors for correction. This targeted approach saves time and reduces the risk of missing critical issues.
Advanced Selection Techniques Within Go To Special
Go To Special goes beyond basic cell types. You can select cells based on their relationship to others, such as identifying cells that differ from their neighbors. This is invaluable for spotting inconsistencies or tracking changes.
Tracing formula relationships also becomes easy. You can instantly select all cells feeding into a specific formula, or all cells affected by a particular cell's value. This provides insights into your calculations' structure and flow. Check out these tips for working with visible cells: How to master working with visible cells in Excel. Combining these skills with Go To Special provides even more control over your data.
Combining Go To Special Operations for Complex Selections
The real strength of Go To Special is the ability to combine multiple operations. For instance, selecting all blank cells within a range that also have conditional formatting would be incredibly difficult manually. By strategically combining Go To Special selections, you can isolate these cells with just a few clicks. This level of control unlocks new possibilities for data manipulation and analysis. This becomes incredibly helpful for tasks like auditing complex financial models or thoroughly checking imported datasets before analysis or presentations.
Real-World Applications of Go To Special
These advanced selection capabilities are particularly useful for professionals working with large, complex spreadsheets. Financial analysts can use Go To Special to audit formulas and ensure model integrity. Data scientists can identify and correct inconsistencies before analysis. These are just a few examples of how Go To Special enhances Excel usage.
Microsoft Office 365 currently holds approximately 29% of the office productivity software market, slightly behind Google's combined offerings at 48% of the broader market. More detailed statistics can be found here: Worldwide Market Share of Office Productivity Software. This widespread use highlights the importance of mastering tools like Go To Special to maximize productivity and efficiency in Excel. By utilizing its full potential, you'll be well on your way to becoming an Excel power user.
Solving Common Find And Select Frustrations
Even seasoned Excel users occasionally run into snags with find and select. This section explores those real-world issues that can cause frustration. We'll look at why seemingly obvious matches sometimes go unfound, often due to hidden characters, formatting discrepancies, or limitations in the search area.
Troubleshooting Unexpected Results
Find and Replace operations don't always give you what you expect. This can happen for several reasons. Hidden characters, like extra spaces or non-printing characters, can lurk in your data, interfering with searches.
Another common issue is formatting conflicts. Searching for "123" as a number might not locate "123" formatted as text. The defined scope of your search also matters. Searching within a specific sheet won't find matches elsewhere in the workbook.
Troubleshooting involves checking for these common problems. Examine your data for hidden characters, double-check formatting consistency, and ensure your search scope is set correctly. These diagnostic steps will save you time and headaches. Learn more in our article about How to master pristine data.
Recovering From Mass Replacement Errors
Mass replacements are efficient, but risky. One wrong move can lead to unwanted changes across your spreadsheet. This is where recovery strategies are crucial. Excel's Undo (Ctrl+Z) is your first line of defense.
However, if you've saved the file after the erroneous replacement, Undo won't work. In these cases, restoring from a recent backup is the safest option. If no backup exists, comparing with earlier versions (if available) or carefully reversing the changes with Find and Replace can help, though it takes more effort. These situations highlight the importance of planning and testing large-scale Find and Replace operations.
Optimizing Performance and Compatibility
Find and select operations can be slow in large Excel files. Optimizing performance involves techniques like breaking large searches into smaller, more manageable parts. This reduces strain on Excel's memory. Closing unnecessary applications or files can also free up system resources.
Compatibility issues can arise when working across different Excel versions. Newer features might not be supported in older versions, leading to unexpected search results or errors. Sticking to basic find and select features, or ensuring everyone uses compatible versions, can prevent these problems.
Common Problems and Their Solutions
The following table details common find and select problems, their symptoms, potential causes, and effective solutions. It provides a quick reference for resolving these issues.
| Problem | Symptoms | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Search Not Finding Matches | Obvious matches are not highlighted | Hidden characters, formatting mismatch, incorrect scope | Use TRIM function, check formatting consistency, verify search scope |
| Unexpected Replacements | Data is altered unintentionally | Incorrect Find and Replace parameters | Use Undo (Ctrl+Z), restore backup, reverse replacements |
| Slow Performance | Find and select operations take a long time | Large file size, memory limitations | Break down searches, close unnecessary applications |
| Compatibility Issues | Inconsistent results across different versions | Incompatible features used across different Excel versions | Use basic features, ensure compatible versions |
This table offers a concise overview of common issues and troubleshooting steps, enabling quicker problem resolution. By understanding these common pitfalls and their solutions, you can use find and select in Excel with more confidence and efficiency. Ready to enhance your Excel skills? Visit SumproductAddict for a curated collection of Excel-themed gear and accessories.